Phenotypes associated with this allele
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn mutation
(3 available);
any
Slc6a3 mutation
(66 available)
|
|
|
normal phenotype
|
|
• homozygous and heterozygous mice are normal and viable
|
behavior/neurological
|
|
• mice exhibit a decline in motor activity and coordination by 2 months of age, maximum decline is reached by 4 months of age
|
|
|
• mice are not able to perform the pole test by 2 months of age, however, treatment with high dose L-DOPA (25 mg/kg) or pioglitazone improves performance
• impaired rotarod performance by 2 months of age, however, treatment with high dose L-DOPA (25 mg/kg) or pioglitazone improves performance
• walking time is decreased on rotarod at 4 and 6 months as compared to younger animals
|
|
|
• decrease in rearing activity by 2 months of age, maximum decline is reached by 4 months of age
|
|
|
• mice move less during nocturnal cycle and in open field test (distance travelled) as compared to controls; treatment with high dose L-DOPA (25 mg/kg) results in hyperactivity and stereotypic movements
• maximum decline in motor performance is reached at 4 months of age
|
hematopoietic system
|
|
• activation of microglial cells in midbrain as detected by Iba1 immunoreactivity
• treatment with pioglitazone for 4 months results in reduction in Iba1 immunoreactivity in midbrain
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• pups are born at a lower body weight than controls and remain at a lower weight throughout life
• administration of pioglitazone increases weight to control levels
|
immune system
|
|
• activation of microglial cells in midbrain as detected by Iba1 immunoreactivity
• treatment with pioglitazone for 4 months results in reduction in Iba1 immunoreactivity in midbrain
|
|
|
• CXCL10 and CCL2 are increased in striatum
• in midbrain, levels of IL6, IL10, CXCL10 and CCL2 trend upward, but do not reach significance
|
|
|
• increase in IL1B in midbrain in 2 month old mice
• IL1B is slightly increased in striatum but does not reach significance
|
homeostasis/metabolism
nervous system
|
|
• activation of microglial cells in midbrain as detected by Iba1 immunoreactivity
• treatment with pioglitazone for 4 months results in reduction in Iba1 immunoreactivity in midbrain
|
|
|
• substantial loss of dopaminergic cell bodies in the substantial nigra as measured by reduction of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and dopamine transporter (DAT) content
• widespread axonal degeneration in striatum
|
behavior/neurological
|
|
• locomotor activity is increased 1.4-fold at low doses in cocaine-treated mice unlike in similarly treated control mice
• at higher doses, cocaine-induced hyperactivity is 3.8-fold compared to 2.8-fold in similarly treated control mice
|
|
|
• mice exhibit increased motivation to work for food compared with control mice
• however, mice exhibit normal profile of loss of responding following cessation of reward delivery
|
|
|
• in an open field that is insensitive to quinpirole treatment
• however, habituation is normal
|
|
|
• locomotor activity is increased 1.4-fold at low doses in cocaine-treated mice unlike in similarly treated control mice
• at higher doses, cocaine-induced hyperactivity is 3.8-fold compared to 2.8-fold in similarly treated control mice
|
nervous system
|
|
• quinpirole fails to induce a slow hyperpolarizing current in dopaminergic neurons unlike in similarly treated control cells
• however, response to baclofen is normal
|
|
|
• decreased and insensitive to sulpiride
|
|
|
• during train stimulation, mice exhibit supramaximal dopamine release that increases during stimulation that is insensitive to sulpiride unlike in control mice
|
homeostasis/metabolism
mortality/aging
|
|
• mutants die around 6-7 weeks of age due to malnutrition; this is most likely due to difficulty accessing food and water in normal cages due to a rearing defect
• however, when mutants are supplied with hydrated gel packs and crushed pieces of regular chow, all mutants survive beyond 6 months of age, with a majority surviving past 1 year of age
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• mutants are significantly smaller than controls by 5 weeks of age
|
|
|
• mutants do not gain weight after 4 weeks of age
|
behavior/neurological
|
|
• mutants are hunched by 5 weeks of age
|
|
|
• severe rearing defect as early as 4 weeks of age
• treatment of mutants with L-DOPA alleviates the motor defects
|
|
|
• mutants are hypoactive by 5 weeks of age
• at 4-5 weeks of age, mutants travel only 68% of the distance traveled by wild-type mice and by 8-11 weeks of age, the distance traveled reduces to 34% of wild-type, indicating an age-dependent decline in locomotive activity
|
|
|
• beginning at 4-5 weeks, mutants exhibit progressive bradykinesia
• mutants exhibit a decline in the speed of movement with age compared to controls
• mutants spend twice as much time inactive at 6-7 weeks of age as controls and by 8-11 weeks of age, this increases to 6-fold increase in inactive time
|
nervous system
|
|
• loss of dopaminergic terminals in the striatum, with a 25% reduction in dopaminergic terminals at 3 weeks of age and 76% reduction by 8-10 weeks
|
|
|
• mutants exhibit loss of dopaminergic efferents to the striatum, with a 25% reduction in dopaminergic terminals at 3 weeks of age and a 76% reduction by 8-10 weeks of age
• however, projections to the nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle are protected and the dopaminergic terminals are moderately preserved at 11-14 weeks
|
|
|
• dopaminergic neurons remaining have smaller cell bodies and diminished neuronal processes
• dopaminergic neurons exhibit mitochondrial fragmentation and depletion
|
|
|
• retrograde degeneration of substantia nigra pars compacta dopaminergic neurons and to a lesser extent in the mesolimbic pathway
|
|
|
• progressive, retrograde degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the nigrostriatal circuit, with neuronal loss first seen at 10-12 weeks, when a 52% decrease in TH-positive neurons is seen
• some degeneration is also seen in the mesolimbic pathway, although a lesser extent than in the nigrostriatal circuit
• degeneration of dopaminergic neurons occurs in a stepwise manner, with initial defects at the axon terminals, followed 1-2 months later by degeneration of the cell bodies
|
|
|
• mutants show decreased mitochondrial transport along nerve processes
|
cellular
|
|
• dopaminergic neurons exhibit mitochondrial fragmentation and depletion
|
skeleton
normal phenotype
|
|
• mice show no abnormal phenotype up to 1 year of age
|
nervous system
|
|
• MPTP-treated mice exhibit reduced numbers of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ neurons and GFP+ TH+ neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) compared with similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
• the percentage of GFP+ glyco-Slc6a3 (DAT)+ neurons is higher than in control mice
|
homeostasis/metabolism
cellular
|
|
• MPTP-treated mice exhibit reduced numbers of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ neurons and GFP+ TH+ neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) compared with similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
• the percentage of GFP+ glyco-Slc6a3 (DAT)+ neurons is higher than in control mice
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1.1(Otx2)Daac mutation
(0 available);
any
Gt(ROSA)26Sor mutation
(942 available)
Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn mutation
(3 available);
any
Slc6a3 mutation
(66 available)
|
|
|
nervous system
|
|
• MPTP-treated mice exhibit increased number of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) compared with Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn heterozygotes
|
|
|
• mice exhibit a reduction in the percentage of Kcnj6 (Girk2)+ or glyco-Slc6a3 (DAT)+ and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) compared with wild-type mice
|
homeostasis/metabolism
cellular
|
|
• MPTP-treated mice exhibit increased number of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) compared with Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn heterozygotes
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1.1(Otx2)Daac mutation
(0 available);
any
Gt(ROSA)26Sor mutation
(942 available)
Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn mutation
(3 available);
any
Slc6a3 mutation
(66 available)
|
|
|
nervous system
|
|
• MPTP-treated mice exhibit a modest increased number of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) compared with Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn heterozygotes
|
homeostasis/metabolism
cellular
|
|
• MPTP-treated mice exhibit a modest increased number of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) compared with Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn heterozygotes
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1.1(Otx2)Daac mutation
(0 available);
any
Gt(ROSA)26Sor mutation
(942 available)
Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn mutation
(3 available);
any
Slc6a3 mutation
(66 available)
Tg(CAG-Otx2,-GFP)21Asim mutation
(1 available)
|
|
|
nervous system
|
|
• MPTP-treated mice exhibit increased number of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) compared with Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn heterozygotes
|
|
|
• mice exhibit a reduction in the percentage of Kcnj6 (Girk2)+ or glyco-Slc6a3 (DAT)+ and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) compared with wild-type mice
|
homeostasis/metabolism
cellular
|
|
• MPTP-treated mice exhibit increased number of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) compared with Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn heterozygotes
|
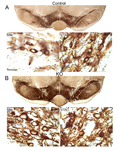
Altered dopamine neurons in the ventral midbrain of Ptentm1Hwu/Ptentm1Hwu Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn/Slc6a3+ mice
behavior/neurological
|
N |
• no difference in locomotor activity is seen compared to controls during exposure to a novel environment
|
|
|
• mutants exhibit a significant reduction in ipsilateral rotational behavior in response to amphetamine administration after 6OHDA lesioning
|
nervous system
|
|
• neuronal hypertrophy in the ventral midbrain resulting in enlargement of the ventral midbrain area
• increase in the number of TH positive neurons in the substantia nigra compacta and ventral tegmental area of the adult ventral midbrain and an increase in neuronal soma size
|
|
|
• increase in the number of TH positive neurons in the substantia nigra compacta
|
|
|
• increase in the number of dopaminergic neuron dendritic processes in the substantia nigra pars reticulata
|
|
|
• modest but significant enlargement of the caudal striatum
|
|
|
• increase in number of dopaminergic neurons and fibers in the ventral mesencephalon
• dopaminergic neurons in the ventral midbrain are larger in size and have an increase in the number of dendritic processes in the substantia nigra pars reticulata
|
|
|
• hypertrophy of dopamine neurons
|
|
|
• mutant dopamine neurons are protected from 6OHDA induced lesions, fiber loss, and axonal loss in the striatum compared to controls
|
homeostasis/metabolism
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Kcnj6em1.1Ktaka mutation
(0 available);
any
Kcnj6 mutation
(26 available)
Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn mutation
(3 available);
any
Slc6a3 mutation
(66 available)
|
|
|
behavior/neurological
|
|
• mice show decreased immobility time in the forced swimming test
• however, locomotor activity in the open field is normal and mice show normal general behaviors such as gait posture
|
nervous system
|
|
• dopamine and baclofen both fail to cause currents in single putative dopamine neurons from the ventral tegmental area
• however, glutamic acid causes currents to the same extent as that in VTA neurons from controls
|



