Phenotypes associated with this allele
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Egln1tm1.1Brei mutation
(0 available);
any
Egln1 mutation
(21 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
|
N |
• mice exhibit normal cardiac response to increased afterload
|
|
|
• capillary area is increased compared to in wild-type hearts
• however, capillary number is normal
|
|
|
• following ligation of the left anterior descending artery
|
|
|
• following ligation of the left anterior descending artery, mice exhibit decreased area at risk, area of necrosis, apoptosis, and reduced decrease in fractional shortening compared with similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
• following ligation of the left anterior descending artery, mice exhibit decreased area at risk and area of necrosis compared with similarly treated wild-type mice
|
homeostasis/metabolism
muscle
|
|
• following ligation of the left anterior descending artery
|
cellular
|
|
• following ligation of the left anterior descending artery
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
Nkx2-5tm1Krc mutation
(0 available);
any
Nkx2-5 mutation
(21 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• incomplete penetrance; mice were born at 78% of the expected rate
• pernatal lethality was reported to be more penetrant with contributions from the C57BL/6 genetic background
|
cardiovascular system
|
N |
• no atrial or ventricular septal defects
|
|
|
• bundle of His was hypoplastic at birth
|
|
|
• atrioventricular (AV) node was hypoplastic at birth
|
|
|
• loss of integrity and sarcomeric structure in conduction system cardiomyocytes
• surrounding, non-conducting, cardiomyoctes were unaffected
|
|
|
• hypertrabeculation; trabecular muscle overgrowth, filling the left ventricle
|
|
|
• progressive AV block associated with cardiomyocyte dropout and fibrosis in the central conduction system
|
homeostasis/metabolism
muscle
|
|
• bundle of His was hypoplastic at birth
|
|
|
• atrioventricular (AV) node was hypoplastic at birth
|
|
|
• loss of integrity and sarcomeric structure in conduction system cardiomyocytes
• surrounding, non-conducting, cardiomyoctes were unaffected
|
|
|
• hypertrabeculation; trabecular muscle overgrowth, filling the left ventricle
|
growth/size/body
cellular
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Hcn4tm1Jsr mutation
(0 available);
any
Hcn4 mutation
(67 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• homozygous embryos die between E9.5 and E11.5
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• high doses of epinephrine in combination with exercise can induce sudden cardiac death in mutants that is not seen in controls
|
|
|
• susceptibility to postnatal lethality from 1 month of age onwards, with 50% dying within 2 months of age and 100% mortality by 5 months of age
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• fatty deposition is seen in the subepicardium, mid-wall region of hearts and in the left ventricle
|
|
|
• in severely affected regions, hearts show some loss of muscle architecture
|
|
|
• rupture of desmosomes and loss of myocyte-myocyte adhesion between neighboring cells as indicated by intercellular gaps in hearts
|
|
|
• defects in intercalated disc integrity as early as 2.5 weeks of age
|
|
|
• pronounced pockets of fat deposition are seen within the subepicardium of hearts from 6 week old mice
|
|
|
• 4 week old mice exhibit enlarged hearts
|
|
|
• right and left ventricular chamber dilation in 4 week old mice which is more pronounced in the right ventricle
|
|
|
• extensive fibrosis in the heart, seen in the right and left ventricles and in the septum, but not in the atria
|
|
|
• mice exhibit increased end-diastolic and end-systolic volumes, reduced ejection fraction, and reduced wall thickness in both the right and left ventricle indicating biventricular dilation and depressed systolic function
|
|
|
• mice exhibit ventricular arrhythmias that are exacerbated with exercise and catecholamine stimulation
• however, mice exhibit normal heart rate
|
|
|
• spontaneous ectopic premature ventricular contractions
|
|
|
• epicardial pattern of action potential propagation following ventricular epicardial pacing shows that mutant hearts display pronounced conduction breaks in wavefront propagation within the epicardium
• analysis of action potential propagation in hearts shows prolonged activation time, action potential durations, and action potential dispersion
|
|
|
• hearts exhibit delayed conduction in the right ventricle following atrial pacing, consistent with right bundle branch block
|
|
|
• increase in QRS intervals, suggestive of ventricular depolarization delay
|
|
|
• mice exhibit a severe form of ventricular cardiomyopathy similar to a biventricular form of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
|
cellular
|
|
• hearts show an increase in TUNEL+ cells in the cardiac mid-wall and in the subepicardial region of the heart, indicating increased apoptosis
|
muscle
|
|
• in severely affected regions, hearts show some loss of muscle architecture
|
|
|
• rupture of desmosomes and loss of myocyte-myocyte adhesion between neighboring cells as indicated by intercellular gaps in hearts
|
|
|
• defects in intercalated disc integrity as early as 2.5 weeks of age
|
|
|
• mice exhibit increased end-diastolic and end-systolic volumes, reduced ejection fraction, and reduced wall thickness in both the right and left ventricle indicating biventricular dilation and depressed systolic function
|
|
|
• mice exhibit a severe form of ventricular cardiomyopathy similar to a biventricular form of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
• loss or thickening of Z-lines in severely affected regions of the heart
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• 4 week old mice exhibit enlarged hearts
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
Vdrtm1.1Sgcg mutation
(0 available);
any
Vdr mutation
(35 available)
Vdrtm1.2Sgcg mutation
(0 available);
any
Vdr mutation
(35 available)
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
|
N |
• untreated and isoflurane-treated mice exhibit normal left ventricular systolic and diastolic function
|
|
|
• in untreated and isoflurane-treated mice
|
|
|
• in untreated and isoflurane-treated mice
|
|
|
• untreated and isoflurane-treated mice exhibit a reduction in end-diastolic volume and end-systolic volume compared with control mice
|
|
|
• in untreated and isoflurane-treated mice
|
|
|
• in untreated and isoflurane-treated mice
|
|
|
• untreated and isoflurane-treated mice exhibit increased thickness of the posterior left ventricular free wall compared with control mice
|
homeostasis/metabolism
endocrine/exocrine glands
|
N |
• unlike null homozygotes, mice do not develop hyperparathyroidism
|
muscle
|
|
• in untreated and isoflurane-treated mice
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• in untreated and isoflurane-treated mice
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Erbb2tm1Cbm mutation
(0 available);
any
Erbb2 mutation
(59 available)
Erbb2tm2Cbm mutation
(0 available);
any
Erbb2 mutation
(59 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• 27% die before reaching 6 months of age and 20% die during echochardiographic or ECG examination
|
|
|
• 16% die within the first 2 weeks, the rest reach adulthood
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• adults and 3 month old mice exhibit myofiber hypertrophy
• frequently observe enlarged cardiomyocyte nuclei with abnormal morphology
|
|
|
• heart-to-body weight ratios of adults are increased by 26%, indicative of hypertrophy
|
|
|
• adults exhibit enlarged ventricular chambers
|
|
|
• progressive malfunction of the heart
|
|
|
• at 1 month of age, see dilatation and loss of left ventricle contractility
• at 3 months of age, ventricular diameter is increased and fractional shortening is impaired
• hearts do not compensate after aortic banding but display a further decrease in fractional shortening
|
|
|
• significantly lengthened QTc interval caused by a slowed ventricular repolarization
|
muscle
|
|
• adults and 3 month old mice exhibit myofiber hypertrophy
• frequently observe enlarged cardiomyocyte nuclei with abnormal morphology
|
|
|
• progressive malfunction of the heart
|
|
|
• at 1 month of age, see dilatation and loss of left ventricle contractility
• at 3 months of age, ventricular diameter is increased and fractional shortening is impaired
• hearts do not compensate after aortic banding but display a further decrease in fractional shortening
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• heart-to-body weight ratios of adults are increased by 26%, indicative of hypertrophy
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• cardiomyocytes of older mutants (9 months of age) exhibit increased length but not width
|
|
|
• myocardium of older mutants (9 months of age) shows disorganized myofibrils with increased nonmyofibrillar space filled with swelled mitochondria
|
|
|
• develop eccentric cardiac hypertrophy (normal left ventricle wall thickness and increased left chamber dimension) upon stimulation with angiotensin II or pressure overload by transverse aortic constriction, exhibiting an increase in heart/body weight ratios and elevated markers of cardiac hypertrophy
|
|
|
• older mutants develop spontaneous cardiac chamber dilation
|
|
|
• develop multifocal interstitial fibrosis upon stimulation with angiotensin II
|
muscle
|
|
• cardiomyocytes of older mutants (9 months of age) exhibit increased length but not width
|
|
|
• myocardium of older mutants (9 months of age) shows disorganized myofibrils with increased nonmyofibrillar space filled with swelled mitochondria
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• develop eccentric cardiac hypertrophy (normal left ventricle wall thickness and increased left chamber dimension) upon stimulation with angiotensin II or pressure overload by transverse aortic constriction, exhibiting an increase in heart/body weight ratios and elevated markers of cardiac hypertrophy
|
cellular
|
|
• develop multifocal interstitial fibrosis upon stimulation with angiotensin II
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Gna11tm1Soff mutation
(0 available);
any
Gna11 mutation
(21 available)
Gnaqtm2Soff mutation
(0 available);
any
Gnaq mutation
(24 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• about 75% die perinatally
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• pups that die perinatally exhibit varying degrees of myocardial hypoplasia
• however, mutants that survive to adulthood, appear normal and are fertile
|
|
|
• homozygotes surviving to adulthood exhibit no ventricular hypertrophy in response to pressure-overload induced by aortic constriction, indicating a complete lack of a hypertrophic response
|
homeostasis/metabolism
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Atp2a2tm1.1Iemr mutation
(0 available);
any
Atp2a2 mutation
(76 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
|
N |
• mice exhibit normal heart weight and cardiac function
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
Txnrd2tm1.1Marc mutation
(0 available);
any
Txnrd2 mutation
(18 available)
Txnrd2tm1Marc mutation
(0 available);
any
Txnrd2 mutation
(18 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• mutants die within several hours after birth
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• myocardial cells are severely distorted with pycnotic nuclei, cytoplasmic vacuolization, reduced cross-striation, and swollen or destroyed mitochondrial cristae
|
|
|
• mutants show clinical features of congestive heart failure
|
homeostasis/metabolism
liver/biliary system
muscle
|
|
• myocardial cells are severely distorted with pycnotic nuclei, cytoplasmic vacuolization, reduced cross-striation, and swollen or destroyed mitochondrial cristae
|
cardiovascular system
|
N |
• no differences in heart shape or in the cellular morphology of cardiomyocytes
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• myocardial cell degeneration marked by eosinophilic myocytes, infiltration of mononuclear cells and significant focal collagen deposition at 10 months of age
• mutants exhibit focal patches of cardiac myocyte membrane damage due to damage expansion of myocardial damage to neighboring myocytes, compared to controls that only show damage in individual myocytes
|
|
|
• some hearts exhibit focal thinning of the left ventricular wall
|
|
|
• increase in cardiac fibrosis, with nearly 9% of the myocardium replaced with focal fibrotic tissue at 10 months of age
|
|
|
• mutants develop progressive dilated cardiomyopathy
• 65% increase in heart weight/body weight ratios
• ratio of the end diastolic volume to mass is increased, indicating dilation of chambers as opposed to increase in overall heart size
• first signs of cardiomyopathy are seen at 7 months of age, with mutants starting to show small focal areas of fibrosis
|
|
|
• reduction in the left ventricular ejection fraction indicating impaired systolic function
|
muscle
|
|
• myocardial cell degeneration marked by eosinophilic myocytes, infiltration of mononuclear cells and significant focal collagen deposition at 10 months of age
• mutants exhibit focal patches of cardiac myocyte membrane damage due to damage expansion of myocardial damage to neighboring myocytes, compared to controls that only show damage in individual myocytes
|
|
|
• mutants develop progressive dilated cardiomyopathy
• 65% increase in heart weight/body weight ratios
• ratio of the end diastolic volume to mass is increased, indicating dilation of chambers as opposed to increase in overall heart size
• first signs of cardiomyopathy are seen at 7 months of age, with mutants starting to show small focal areas of fibrosis
|
|
|
• reduction in the left ventricular ejection fraction indicating impaired systolic function
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Ldb3tm4Chen mutation
(0 available);
any
Ldb3 mutation
(46 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• all die between 16 and 23 weeks of age
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• Z-lines in 3 month old mice are severely disrupted and disorganized and abnormal mitochondria are seen
• however M-lines are relatively normal
|
|
|
• enlarged left and right ventricles
|
|
|
• the ratios of heart weight to body weight and heart weight to tibia bone length are increased
|
|
|
• thinner at end diastole compared to controls
|
|
|
• enlarged with a thinner wall
• increase in left ventricle size is seen in mice at 2 - 4 months of age but not at 1 month of age
• significant increase in left ventricular dimension at end diastole and end systole
|
|
|
• enlarged with a thinner wall
|
|
|
• in both the left and right ventricles
|
|
|
• electrocardiography reveals an atrioventricular block
|
muscle
|
|
• Z-lines in 3 month old mice are severely disrupted and disorganized and abnormal mitochondria are seen
• however M-lines are relatively normal
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• enlarged left and right ventricles
|
|
|
• the ratios of heart weight to body weight and heart weight to tibia bone length are increased
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Itgb1tm1Ross mutation
(0 available);
any
Itgb1 mutation
(59 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• after 7 days of aortic constriction, only 53% of mutants survive compared to 88% of controls
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• show liver congestion at about 6 months of age
|
|
|
• myocardium shows focal dissolution of myofibrils and intercalated disks as well as mitochondrial swelling, with disruption and loss of cristae
|
|
|
• heart sections show disruption of myocyte cell membrane integrity
|
|
|
• enlarged at around 6 months of age
|
|
|
• calcification within the ventricular wall at about 6 months of age
|
|
|
• adults develop patchy fibrosis in the ventricular wall
• hearts show replacement fibrosis at around 6 months of age
|
|
|
• dilation at about 6 months of age
|
|
|
• display abnormal glucose metabolism in the ventricular tissue with patchy uptake of fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) throughout the ventricular myocardium
|
|
|
• contractility of the left ventricle is impaired at 5 weeks of age, however left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and heart rate do not vary from controls
|
|
|
• relaxation of the left ventricle is impaired at 5 weeks of age
|
|
|
• hemodynamic loading imposed by 7 days of transverse aortic constriction shows that mutants are intolerant of this stress as they have 53% survival versus 88% in controls
|
|
|
• show signs of congestive heart failure when reach about 6 months of age, including pleural effusions and liver congestion
|
homeostasis/metabolism
liver/biliary system
|
|
• show liver congestion at about 6 months of age
|
muscle
|
|
• myocardium shows focal dissolution of myofibrils and intercalated disks as well as mitochondrial swelling, with disruption and loss of cristae
|
|
|
• heart sections show disruption of myocyte cell membrane integrity
|
|
|
• display abnormal glucose metabolism in the ventricular tissue with patchy uptake of fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) throughout the ventricular myocardium
|
|
|
• contractility of the left ventricle is impaired at 5 weeks of age, however left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and heart rate do not vary from controls
|
|
|
• relaxation of the left ventricle is impaired at 5 weeks of age
|
respiratory system
|
|
• show pleural effusions at about 6 months of age
|
cellular
|
|
• display abnormal glucose metabolism in the ventricular tissue with patchy uptake of fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) throughout the ventricular myocardium
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• fewer blood vessels are present in the left ventricle compared to in wild-type mice
|
|
|
• the diastolic thickness of the intraventricular septum is increased compared to in wild-type mice
|
|
|
• left ventricular end-diastolic diameter is reduced compared to in wild-type mice
|
|
|
• the diastolic thickness of the left ventricle is increased compared to in wild-type mice
|
|
|
• mice exhibit reduced fractional shortening compared with wild-type mice
• during electrical stimulation, cardiomyocytes exhibit reduced cell shortening compared with wild-type cells
|
|
|
• dobutamine-treated mice exhibit increased isovolumic relaxation time, a measure of diastolic dysfunction, compared to in similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
• mice exhibit reduced maximum rates of left ventricular pressure development and pressure decline compared to in wild-type mice
|
|
|
• cardiomyocytes exhibit prolonged time to reduce cytosolic calcium levels compared with wild-type cells
|
growth/size/body
homeostasis/metabolism
muscle
|
|
• mice exhibit reduced fractional shortening compared with wild-type mice
• during electrical stimulation, cardiomyocytes exhibit reduced cell shortening compared with wild-type cells
|
|
|
• dobutamine-treated mice exhibit increased isovolumic relaxation time, a measure of diastolic dysfunction, compared to in similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Erbb4tm1Htig mutation
(0 available);
any
Erbb4 mutation
(87 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• die within the first year of life
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• cardiomyocyte length is increased and they exhibit enlarged nuclei with a significantly higher rate of polyploidy at 3 months of age
• dilation of tubular membrane system in myocytes with normal myofibrils and mitochondria
|
|
|
• number of intercalated disks per unit area of ventricular muscle is reduced
|
|
|
• number of nuclei per unit area of ventricular muscle is reduced
|
|
|
• exhibit higher heart-to-body weight ratios than wildtype at 3 months of age
|
|
|
• hearts are enlarged, however observe no differences in cardiomyocyte cell number, proliferation or apoptosis
|
|
|
• dilation evident by 3 months of age but is not seen in neonates
|
|
|
• evident by 3 months of age
|
|
|
• dilation evident by 3 months of age but is not seen in neonates
|
|
|
• retrograde perfusion of the left ventricle in isolated hearts shows a reduction of the maximal left ventricular developed pressure, demonstrating depressed myocardial contractility
|
|
|
• programmed intracardiac stimulation shows increased susceptibility to ventricular tachycardia
|
|
|
• ECG at 2-3 months of age shows widened QRS complex and Q-Tc intervals, indicating delayed conduction
|
|
|
• ECG at 2-3 months of age shows widened QRS complex
|
|
|
• 12.5% prolongation in Q-Tc intervals
|
muscle
|
|
• cardiomyocyte length is increased and they exhibit enlarged nuclei with a significantly higher rate of polyploidy at 3 months of age
• dilation of tubular membrane system in myocytes with normal myofibrils and mitochondria
|
|
|
• number of intercalated disks per unit area of ventricular muscle is reduced
|
|
|
• number of nuclei per unit area of ventricular muscle is reduced
|
|
|
• retrograde perfusion of the left ventricle in isolated hearts shows a reduction of the maximal left ventricular developed pressure, demonstrating depressed myocardial contractility
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• exhibit higher heart-to-body weight ratios than wildtype at 3 months of age
|
|
|
• hearts are enlarged, however observe no differences in cardiomyocyte cell number, proliferation or apoptosis
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
Pak1tm1.1Xwg mutation
(0 available);
any
Pak1 mutation
(36 available)
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• increased following transverse aortic constriction and prolonged load stress
• in response to Ang II infusion
|
|
|
• following transverse aortic constriction and prolonged load stress
• in response to Ang II infusion
|
|
|
• following transverse aortic constriction
• in response to Ang II infusion
• treatment with FTY720 does not blocked cardiac hypertrophy induced by transverse aortic constriction
|
|
|
• increased collagen-deposition following prolonged load stress
• in response to Ang II infusion
|
|
|
• following prolonged load stress
• in response to Ang II infusion
|
|
|
• 5-fold increase following transverse aortic constriction
|
|
|
• following transverse aortic constriction, cardiomyocytes exhibit exacerbated pressure overload-induced hypertrophy and increased cardiomyocytes size and apoptosis compared with control mice
• prolonged load stress sensitizes mice to heart failure, pulmonary edema, reduced fractional shortening, increased heart weight, increased myocyte cross-sectional area and collagen deposition
• however, contractile performance is normal following limited transverse aortic contriction
|
|
|
• following prolonged load stress
|
respiratory system
|
|
• following prolonged load stress
|
cellular
|
|
• 5-fold increase following transverse aortic constriction
|
homeostasis/metabolism
muscle
|
|
• increased following transverse aortic constriction and prolonged load stress
• in response to Ang II infusion
|
|
|
• following prolonged load stress
• in response to Ang II infusion
|
|
|
• 5-fold increase following transverse aortic constriction
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• following transverse aortic constriction and prolonged load stress
• in response to Ang II infusion
|
|
|
• following transverse aortic constriction
• in response to Ang II infusion
• treatment with FTY720 does not blocked cardiac hypertrophy induced by transverse aortic constriction
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Mfn2tm1.1Mzhe mutation
(0 available);
any
Mfn2 mutation
(26 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
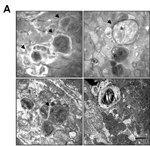
Autophagosome accumulation in Mfn2tm1.1Mzhe/Mfn2tm1.1Mzhe Myl2tm1(cre)Krc/Myl2+ hearts
cardiovascular system
|
|
• cardiomyocytes exhibit increased numbers of large mitochondria and average size of mitochondrial area compared with cells from control mice
• cardiomyocytes contain large numbers of double and multimembrane autophagosome-like vacuolar structures and increased autophagic activity compared with cells from control mice
• cardiomyocytes exhibit impaired autophagosome-lysosome fusion compared with cells from control mice
• cardiomyocytes exhibit endoplasmic reticulum stress unlike cells from control mice
• however, cardiomyocytes exhibit normal mitochondrial mass and autophagosome formation
|
|
|
• beginning at 17 months of age
|
|
|
• at 12 months following ischemia-reperfusion stress
|
|
|
• following ischemia-reperfusion stress, cardiomyocytes from 6 month old mice exhibit a greater loss of mitochondrial membrane potential compared with cells from control mice
• however, mitochondrial membrane potential is normal at 4 months following ischemia-reperfusion stress
|
|
|
• following ischemia-reperfusion stress, cardiomyocytes from 6 month old mice exhibit a greater loss of mitochondrial membrane potential compared with cells from control mice
• worse at 12 months of age with increased cardiomyocytes apoptosis
• however, mitochondrial membrane potential is normal at 4 months following ischemia-reperfusion stress
|
cellular
|
|
• at 12 months following ischemia-reperfusion stress
|
|
|
• cardiomyocytes exhibit increased numbers of large mitochondria and average size of mitochondrial area compared with control mice
• however, mitochondrial mass is normal
|
|
|
• cardiomyocytes contain large numbers of double and multi-membrane autophagosome-like vacuolar structures and increased autophagic activity compared with cells from control mice
• cardiomyocytes exhibit impaired autophagosome-lysosome fusion compared with cells from control mice
• however, autophagosome formation is normal
|
|
|
• decreased respiratory control ration in the cardiomyocytes
|
pigmentation
muscle
|
|
• cardiomyocytes exhibit increased numbers of large mitochondria and average size of mitochondrial area compared with cells from control mice
• cardiomyocytes contain large numbers of double and multimembrane autophagosome-like vacuolar structures and increased autophagic activity compared with cells from control mice
• cardiomyocytes exhibit impaired autophagosome-lysosome fusion compared with cells from control mice
• cardiomyocytes exhibit endoplasmic reticulum stress unlike cells from control mice
• however, cardiomyocytes exhibit normal mitochondrial mass and autophagosome formation
|
|
|
• beginning at 17 months of age
|
homeostasis/metabolism
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Cacnb2tm1.1Mfre mutation
(0 available);
any
Cacnb2 mutation
(50 available)
Cacnb2tm1Mfre mutation
(0 available);
any
Cacnb2 mutation
(50 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
cardiovascular system
|
|
• the beating frequency of E13.5 heart explants is reduced compared to for wild-type hearts
|
|
|
• calcium channel current density is reduced compared to in wild-type mice (-12.3+/-0.6 mV compared to -16.9+/-07 mV in wild-type mice)
|
embryo
|
|
• between E11.5 and E12.5, vascular remodeling of the primary capillary plexus fails to occur and a honeycomb-like network of tubules with enlarged and uniform diameters forms in the extra- and intraembryonic vasculature
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
Tg(Myh6-GFP,MAP2K6)8Ywa mutation
(0 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• hemizygous or homozygous mice for Tg(Myh6-GFP,MAP2K6)8Ywa that are also heterozygous for Myl2tm1(cre)Krc, in which cre mediated recombination is induced in cardiac muscle, display premature death between 5 and 7 weeks of age
|
respiratory system
|
|
• sign of dyspnea around time of death
|
homeostasis/metabolism
cardiovascular system
|
|
• modest increase in myocyte size, and no myocyte atrophy
|
|
|
• profoundly enlarged atria
|
|
|
• increased atrial mass often filled with thrombosis
• external dimensions, and mass of ventricles are normal
|
|
|
• trichrome staining shows substantial interstitial fibrotic tissues
|
|
|
• systolic contractile depression and restrictive diastolic abnormalities
• reduced end-diastolic ventricular cavity size
|
muscle
|
|
• modest increase in myocyte size, and no myocyte atrophy
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• increased atrial mass often filled with thrombosis
• external dimensions, and mass of ventricles are normal
|
cellular
|
|
• trichrome staining shows substantial interstitial fibrotic tissues
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
Tg(Myh6-GFP,MAP2K3)58Ywa mutation
(0 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• hemizygous or homozygous mice for Tg(Myh6-GFP,MAP2K3)58Ywa that are also heterozygous for Myl2tm1(cre)Krc, in which cre mediated recombination is induced in cardiac muscle, display premature death between 5 and 7 weeks of age
|
respiratory system
|
|
• sign of dyspnea around time of death
|
homeostasis/metabolism
cardiovascular system
|
|
• heterogeneous myocyte atrophy
|
|
|
• profoundly enlarged atria
|
|
|
• increased atrial mass often filled with thrombosis
• external dimensions, and mass of ventricles are normal
|
|
|
• trichrome staining shows substantial interstitial fibrotic tissues
|
|
|
• systolic contractile depression and restrictive diastolic abnormalities
• increased end-systolic chamber volumes
|
muscle
|
|
• heterogeneous myocyte atrophy
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• increased atrial mass often filled with thrombosis
• external dimensions, and mass of ventricles are normal
|
cellular
|
|
• trichrome staining shows substantial interstitial fibrotic tissues
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Lims1tm1.1Chen mutation
(0 available);
any
Lims1 mutation
(53 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
|
N |
• exhibit no basal phenotype with regard to mouse survival, cardiac histology or cardiac function
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Erbb2tm1Klee mutation
(0 available);
any
Erbb2 mutation
(59 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• transthoracic arotic banding results in a significant increase in mortality (70%) versus wild-type (10%)
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• increase in the numbers of mitochondria and vacuoles in cardiomyoctyes, however cytoskeletal ultrastructure is unchanged
|
|
|
• increase in apoptosis in the ventricles
|
|
|
• decrease in LV septal thickness
|
|
|
• decrease in LV posterior wall thickness
|
|
|
• mutants display relatively normal function at 6 weeks of age and progressively acquire features of cardiomyopathy over a 6-month period
• exhibit ventricular enlargement of both the left and right cardiac chambers and a marked increase in heart:body weight ratio
|
|
|
• decrease in fractional shortening, velocity of circumferential fiber shortening and a reduction of the maximum first derivative of left ventricle pressure, indicating depressed myocardium contractility, however no differences in heart rate or left ventricle end-diastolic pressure
|
|
|
• reduction in left ventricle dP/dt min indicates impaired left ventricle relaxation
|
muscle
|
|
• increase in the numbers of mitochondria and vacuoles in cardiomyoctyes, however cytoskeletal ultrastructure is unchanged
|
|
|
• mutants display relatively normal function at 6 weeks of age and progressively acquire features of cardiomyopathy over a 6-month period
• exhibit ventricular enlargement of both the left and right cardiac chambers and a marked increase in heart:body weight ratio
|
|
|
• decrease in fractional shortening, velocity of circumferential fiber shortening and a reduction of the maximum first derivative of left ventricle pressure, indicating depressed myocardium contractility, however no differences in heart rate or left ventricle end-diastolic pressure
|
|
|
• reduction in left ventricle dP/dt min indicates impaired left ventricle relaxation
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• homozygous mice die between 6-8 weeks after birth from the heart malfunction with a gender difference (males more severely affected then females)
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• thinner posterior wall of the left ventricle
|
|
|
• seen 6-7 weeks after birth
|
|
|
• cardiomyocytes have fuzzy z-lines and shortened sarcomeres that appear locked in the contracted state
• severe excitation-contraction coupling defect causing a hypercontraction phenotype at the single cell level
|
muscle
|
|
• seen 6-7 weeks after birth
|
|
|
• cardiomyocytes have fuzzy z-lines and shortened sarcomeres that appear locked in the contracted state
• severe excitation-contraction coupling defect causing a hypercontraction phenotype at the single cell level
|
growth/size/body
mortality/aging
|
|
• life span is normal except that pregnancy-induced mortality is seen
|
cardiovascular system
|
N |
• deletion had little affect on cardiomyocyte proliferation or viability
• mutants have a normal heart rate, interventricular septum thickness, and left ventricular posterior wall thickness
|
|
|
• extensive fibrosis and myofibril disarray are evident by trichome staining in older mice
|
|
|
• mutant hearts appear normal initially and become enlarged 5 weeks after birth
• increasing workload and stress results in manifestation of a latent defect in cardiac function
|
|
|
• mutants have a severe contraction defect
• both left ventricular end-diastolic dimensions and end-systolic dimensions are markedly increased 5 to 6 weeks after birth
• the percent fractional shortening and mean velocity of circumferential fiber shortening (indicators of systolic cardiac function) are severely reduced
• in isolated cardiomyocytes resting intracellular and diastolic Ca2+ is normal however, with increasing pacing frequencies a significant decrease in both Ca2+ transients and cell contraction are detected
• defects in Ca2+ relaxation kinetics and reduced Ca2+ transients would weaken the excitation-contraction coupling in response to increasing workload
|
muscle
|
|
• mutant hearts appear normal initially and become enlarged 5 weeks after birth
• increasing workload and stress results in manifestation of a latent defect in cardiac function
|
|
|
• mutants have a severe contraction defect
• both left ventricular end-diastolic dimensions and end-systolic dimensions are markedly increased 5 to 6 weeks after birth
• the percent fractional shortening and mean velocity of circumferential fiber shortening (indicators of systolic cardiac function) are severely reduced
• in isolated cardiomyocytes resting intracellular and diastolic Ca2+ is normal however, with increasing pacing frequencies a significant decrease in both Ca2+ transients and cell contraction are detected
• defects in Ca2+ relaxation kinetics and reduced Ca2+ transients would weaken the excitation-contraction coupling in response to increasing workload
|
cellular
|
|
• extensive fibrosis and myofibril disarray are evident by trichome staining in older mice
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• about 10% of mutants die at 103 +/- 7 days of age
|
|
|
• all (6) mutant females that gave birth died within 9+/-2 days of delivery and 4 mutant females died after mating but before delivery
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• mutants that die at 103 +/- 7 days of age have enlarged hearts
|
|
|
• at 7 - 8 weeks of age, fractional shortening, velocity of circumferential fiber shortening, and ejection fraction are reduced by 30%, 25%, and 21%, respectively; however no signs of hypertrophy are seen at this time
• impairment of cardiac function increases with age
|
|
|
• the decline of caffeine-induced calcium transients is slower in mutant cells and caffeine-induced Na+-Ca2+ exchange current is absent
• current-voltage relationships for voltage-dependent L-type Ca2+ currents are decreased
|
muscle
|
|
• at 7 - 8 weeks of age, fractional shortening, velocity of circumferential fiber shortening, and ejection fraction are reduced by 30%, 25%, and 21%, respectively; however no signs of hypertrophy are seen at this time
• impairment of cardiac function increases with age
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• mutants that die at 103 +/- 7 days of age have enlarged hearts
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• midian survival was 6 months
• none survived past 8 months
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• focal appearance of enlarged cardiac myocytes with apparent vacuoles
• scattered intramural foci of enlarged cells with excess glycogen revealed by histologic studies at 2 and 5 month of age
• there was no evidence of proliferative cardiac tumors
|
|
|
• with heart enlargement and pulmonary congestion
• a significant increase in LV end-diastolic diameter and LV end-systolic diameter, and a reduction in fractional shortening in 2- to 3-month-old mutant mice by echocardiographic analysis
• increase in heart weight, heart/body weight ratio and heart weight/tibial length ratio
|
|
|
• a significant increase in LV end-diastolic diameter and LV end-systolic diameter, and a reduction in fractional shortening in 2- to 3-month-old mutant mice by echocardiographic analysis
|
muscle
|
|
• focal appearance of enlarged cardiac myocytes with apparent vacuoles
• scattered intramural foci of enlarged cells with excess glycogen revealed by histologic studies at 2 and 5 month of age
• there was no evidence of proliferative cardiac tumors
|
|
|
• with heart enlargement and pulmonary congestion
• a significant increase in LV end-diastolic diameter and LV end-systolic diameter, and a reduction in fractional shortening in 2- to 3-month-old mutant mice by echocardiographic analysis
• increase in heart weight, heart/body weight ratio and heart weight/tibial length ratio
|
|
|
• a significant increase in LV end-diastolic diameter and LV end-systolic diameter, and a reduction in fractional shortening in 2- to 3-month-old mutant mice by echocardiographic analysis
|
homeostasis/metabolism
respiratory system
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
Sp4tm2Krc mutation
(0 available);
any
Sp4 mutation
(35 available)
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• in mutants, there is a marked disorganization of a marker for cardiac Purkinje cells Cx40, with it being dispersed throughout the cell instead of localized along the cell boundaries as in wild-type
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• normal hearts at 6 months
• hemosiderin deposition and fibrosis in 3 of 12 hearts examined at 9 months
• isoproterenol treatment of 3 month old mice also results in hemosiderin deposition and fibrosis
|
normal phenotype
|
|
• no defects in heart or body weight parameters or in electrocardiogram analyses are seen in mice between 14 and 40 weeks of age
• suggests that this gene is not required for development or function of the heart after the looping morphogenesis stage
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
F3tm1Nmk mutation
(1 available);
any
F3 mutation
(24 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
Tg(Myh6-F3)4Nmk mutation
(0 available)
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
|
N |
• mice are normal to 6 months of age
|
normal phenotype
|
|
• mutants in which Rxra is specifically deleted in ventricular myocardium are indistinguishable from littermates, grow to adulthood without signs of neonatal dysfunction and hearts do not exhibit any defects, indicating normal fetal ventricular morphogenesis
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• mice exhibit sudden deaths with no symptoms of cardiomyopathy at young ages (6 weeks) and signs of heart failure at older ages (14 months)
• at 14 weeks, 49% of males die suddenly without any defects in cardiac contractile function
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• heart weight to body weight and heart weight to tibia length are increased
|
|
|
• mice exhibit progressive dilation of the left ventricle during systole and diastole that parallels the decline in ventricular function
|
|
|
• mutants that do not die suddenly, develop dilated cardiomyopathy as they age
|
|
|
• as mice age they display reduced percent fractional shortening and velocity of circumferential fiber shortening
|
|
|
• at high doses of dobutamine left ventricle relaxation is abnormal indicating mild diastolic dysfunction
|
|
|
• young mice exhibit polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
|
|
|
• older mice exhibit arrhythmias that are not found in wild-type mice
|
|
|
• 86% of mice exhibit ectopy
• during apical pacing, hearts display a disturbed front wave propagation and greater negative front wave curvature compared to in wild-type mice
|
|
|
• young mice exhibit heart block
|
|
|
• mice that die after 14 weeks exhibit signs, symptoms and postmortem evidence of heart failure
|
muscle
|
|
• mutants that do not die suddenly, develop dilated cardiomyopathy as they age
|
|
|
• as mice age they display reduced percent fractional shortening and velocity of circumferential fiber shortening
|
|
|
• at high doses of dobutamine left ventricle relaxation is abnormal indicating mild diastolic dysfunction
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• heart weight to body weight and heart weight to tibia length are increased
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• higher coronary flow after ischemia/reperfusion injury
|
|
|
• significantly better cardiac function after 30 minutes of ischemia followed by 30 minutes of reperfusion than in controls
• higher left ventricle developed pressure than in controls
• higher rate pressure product
|
homeostasis/metabolism
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Atp1b1tm1.1Akra mutation
(0 available);
any
Atp1b1 mutation
(20 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• following transverse aortic constriction, mice exhibit increased mortality compared to wild-type mice
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• maximum rate of heart contraction and relaxation is increased compared to in wild-type mice
|
|
|
• at 13 to 14 months, mice exhibit decreased fractional shortening, velocity of circumferential fiber shortening, and ejection fraction compared with wild-type mice
• following transverse aortic constriction, mice exhibit decreased fractional shortening, velocity of circumferential fiber shortening, and ejection fraction compared with wild-type mice
• mice treated with ouabain fail to exhibit an increase in maximum rate of heart contraction and relaxation unlike similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
• the amplitude of calcium ion released from cardiomyocyte is increased 1.6-fold compared to in wild-type cells
• time to peak calcium ion release from cardiomyocyte is increased compared to in wild-type cells
|
|
|
• following transverse aortic constriction, mice exhibit signs of heart dysfunction, decreased ventricular function, and increased mortality compared to wild-type mice
|
homeostasis/metabolism
muscle
|
|
• maximum rate of heart contraction and relaxation is increased compared to in wild-type mice
|
|
|
• at 13 to 14 months, mice exhibit decreased fractional shortening, velocity of circumferential fiber shortening, and ejection fraction compared with wild-type mice
• following transverse aortic constriction, mice exhibit decreased fractional shortening, velocity of circumferential fiber shortening, and ejection fraction compared with wild-type mice
• mice treated with ouabain fail to exhibit an increase in maximum rate of heart contraction and relaxation unlike similarly treated wild-type mice
|
growth/size/body
mortality/aging
|
|
• mice die after thoracic transverse aortic constriction of heart failure
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• 1 week following thoracic transverse aortic constriction (TAC) or a 7 day treatment with isoproterenol left ventricular dilation is observed
|
|
|
• thoracic transverse aortic constriction (TAC) and isoproterenol induce severe cardiac dysfunction
|
homeostasis/metabolism
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Fgfr1tm1Upir mutation
(0 available);
any
Fgfr1 mutation
(221 available)
Fgfr2tm1Dor mutation
(3 available);
any
Fgfr2 mutation
(87 available)
Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1(Cdkn1b,EGFP)Dor mutation
(0 available);
any
Gt(ROSA)26Sor mutation
(942 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• mice exhibit smaller hearts than mice homozygous for null alleles of Fgfr1 and Fgfr2 due to decreased myocardial proliferation
• however, coronary development is normal
|
|
|
• mice exhibit thinner ventricular walls than mice homozygous for null alleles of Fgfr1 and Fgfr2
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1(Cdkn1b,EGFP)Dor mutation
(0 available);
any
Gt(ROSA)26Sor mutation
(942 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• mice exhibit small hearts due to decreased myocardial proliferation
• however, coronary development is normal
|
|
|
• the ventricular wall thickness is 67+/-8% of wild-type but not as thin as in homozygotes (54+/-6%)
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1(Cdkn1b,EGFP)Dor mutation
(0 available);
any
Gt(ROSA)26Sor mutation
(942 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• mice exhibit small hearts due to decreased myocardial proliferation
• however, coronary development is normal
|
|
|
• the ventricular wall thickness is 54+/-6% of wild-type mice
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Gja1tm1Gfi mutation
(0 available);
any
Gja1 mutation
(59 available)
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• begin to die at 2-3 weeks of age and all are dead within the first 2 months
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Myl2tm1(cre)Krc mutation
(2 available);
any
Myl2 mutation
(22 available)
Pip5k1ctm2Csab mutation
(0 available);
any
Pip5k1c mutation
(41 available)
|
|
|
hematopoietic system
|
|
• mutant platelets have a membrane-related cytoskeletal defect that might account for the ex vivo adhesion defect
|
|
|
• wild-type platelets adhered to collagen in small clusters, whereas adherent mutant platelets failed to aggregate with other platelets
• mutant mice formed stable thrombi less efficiently than controls; these mice usually formed thrombi as rapidly as wild-type mice, but these vascular occlusions were unstable
|
homeostasis/metabolism



 Analysis Tools
Analysis Tools