Phenotypes associated with this allele
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Aldh1a2tm1Dll mutation
(0 available);
any
Aldh1a2 mutation
(36 available)
|
|
|
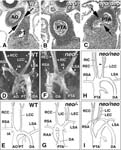
Outflow tract septation defects and abnormal patterns of aortic arch-derived arteries in Aldh1a2tm1Dll/Aldh1a2tm1Dll and Aldh1a2tm1Dll/Aldh1a2tm1Ipc mice
mortality/aging
|
|
• homozygotes are obtained at the expected Mendelian frequencies at E9.5-E12.5 and at E13.5-E14.5
• most homozygotes are alive at E18.5 or P1; however, about 75% of homozygotes die before the age of 2 weeks
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• at E18.5 or P1, all homozygotes display abnormal patterns of the aortic arch and/or head and neck great arteries
|
|
|
• at E18.5 or P1, one of 4 homozygotes shows an abnormally high (cervical) aortic arch and an abnormal origin of the right subclavian artery (RSA), which arise distally as a common stem with the LSA, whereas its carotid arteries arise from a common proximal innominate artery
|
|
|
• at E18.5 or P1, one of 4 homozygotes shows an abnormally high (cervical) aortic arch
|
|
|
• at E18.5 or P1, most homozygotes lack, or have shorter, common carotid arteries, their internal and external carotids arising from the aortic arch, the innominate artery, or at midtracheal (instead of upper cervical) level
|
|
|
• at E18.5 or P1, one of 4 homozygotes displays an ectopic origin of the left subclavian artery from the ductus arteriosus
|
|
|
• at E14.5, 3 of 4 homozygotes exhibit a partially septated outflow tract
|
respiratory system
|
|
• tracheal cartilage ring numbers are only slightly reduced
|
|
|
• at E18.5, homozygotes display a shorter trachea
|
homeostasis/metabolism
growth/size/body
|
|
• at E18.5 or P1, homozygotes are slightly smaller but overtly normal relative to wild-type mice
|
skeleton
|
|
• tracheal cartilage ring numbers are only slightly reduced
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Aldh1a2tm1Dll mutation
(0 available);
any
Aldh1a2 mutation
(36 available)
Aldh1a2tm1Ipc mutation
(0 available);
any
Aldh1a2 mutation
(36 available)
|
|
|

Outflow tract septation defects and abnormal patterns of aortic arch-derived arteries in Aldh1a2tm1Dll/Aldh1a2tm1Dll and Aldh1a2tm1Dll/Aldh1a2tm1Ipc mice
mortality/aging
|
|
• all mutants die before the age of 2 weeks
• however, compound heterozygotes are obtained at the expected Mendelian ratios at E9.5-E12.5 and E13.5-E14.5
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
• at E18.5 or P1, all mutant embryos show abnormal patterns of the aortic arch and/or head and neck great arteries
|
|
|
• at E11.5, a single, enlarged vessel caudal to the third arches is observed instead of the distinct fourth and sixth aortic arches observed in wild-type embryos
|
|
|
• at E9.5, no third aortic arches are formed; however, third aortic arches are detectable at E10.5
|
|
|
• in mutants, the right subclavian artery (RSA) originates ectopically from the descending aorta
|
|
|
• at E18.5 or P1, two of 7 mutants show a right-sided aortic arch, one with a double arch
|
|
|
• at E18.5 or P1, one of 7 mutants shows a double aortic arch
|
|
|
• at E18.5 or P1, most mutants lack, or have shorter, common carotid arteries, their internal and external carotids arising from the aortic arch, the innominate artery, or at midtracheal (instead of upper cervical) level
|
|
|
• in mutants, the left subclavian artery (LSA) and left carotid arteries arise from a common trunk or innominate artery
|
|
|
• at E14.5, two of 7 mutant embryos exhibit poorly developed conotruncal wedges
|
|
|
• at E14.5, five of 7 mutant embryos display a completely unseptated outflow tract (PTA)
|
|
|
• at E14.5, all mutant embryos exhibit a ventricular septal defect
|
embryo
|
|
• at E11.5, a single, enlarged vessel caudal to the third arches is observed instead of the distinct fourth and sixth aortic arches observed in wild-type embryos
|
|
|
• at E9.5, no third aortic arches are formed; however, third aortic arches are detectable at E10.5
|
|
|
• at E9.5, mutant embryos show abnormal NCC patterning caudally to the second branchial arch; instead of forming separate streams colonizing the third and fourth to sixth arches, NCCs are arranged in a single mass which is poorly connected with the hindbrain
• in contrast, the migratory pathways of more rostral NCC populations (i.e. toward branchial arches 1 and 2) appear normal
|
|
|
• at E9.5, mutant embryos show an apparent lack of third branchial arches
|
|
|
• at E9.5, mutants exhibit significant hypoplasia of the putative third and fourth to sixth arches, despite the presence of identifiable ectodermal clefts
• in addition, abnormal fusion of the second and third epibranchial placodes is noted at E9.5
|
|
|
• at E9.5, the second pharyngeal pouch is properly formed; however, no signs of distinct third or fourth pharyngeal pouches are observed
|
respiratory system
|
|
• at E18.5, mutants display highly abnormal laryngeal cartilages
|
|
|
• at E18.5, the posterior aspect of cricoid cartilage is abnormally segmented into ring-like structures
|
|
|
• at E18.5, an ectopic cartilage connects the hyoid bone and thyroid cartilage
|
|
|
• at E18.5, mutants display highly abnormal, reduced tracheal rings
|
|
|
• at E18.5, mutants display a short trachea
|
immune system
|
|
• at E18.5, nine of 10 mutants exhibit display aplasia or significant hypoplasia of the thymus
|
|
|
• at E18.5, nine of 10 mutants exhibit display aplasia or significant hypoplasia of the thymus
|
endocrine/exocrine glands
|
|
• at P1, mutants show absence of parathyroid glands, despite a well-formed thyroid gland
|
|
|
• at E18.5, nine of 10 mutants exhibit display aplasia or significant hypoplasia of the thymus
|
|
|
• at E18.5, nine of 10 mutants exhibit display aplasia or significant hypoplasia of the thymus
|
nervous system
|
|
• at E9.5, mutant embryos display defective cranial nerve developmental in the postotic branchial region
|
|
|
• at E11.5, mutant embryos display abnormal fusion of cranial nerves IX (glosso-pharyngeal) and X (vagus) in a single bundle and failure to form separate distal ganglia
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• at E18.5 or P1, most mutants are slightly smaller but overtly normal relative to wild-type mice
|
homeostasis/metabolism
craniofacial
|
|
• at E11.5, a single, enlarged vessel caudal to the third arches is observed instead of the distinct fourth and sixth aortic arches observed in wild-type embryos
|
|
|
• at E9.5, no third aortic arches are formed; however, third aortic arches are detectable at E10.5
|
|
|
• at E9.5, mutant embryos show an apparent lack of third branchial arches
|
|
|
• at E9.5, mutants exhibit significant hypoplasia of the putative third and fourth to sixth arches, despite the presence of identifiable ectodermal clefts
• in addition, abnormal fusion of the second and third epibranchial placodes is noted at E9.5
|
skeleton
|
|
• at E18.5, mutants display highly abnormal laryngeal cartilages
|
|
|
• at E18.5, the posterior aspect of cricoid cartilage is abnormally segmented into ring-like structures
|
|
|
• at E18.5, an ectopic cartilage connects the hyoid bone and thyroid cartilage
|
|
|
• at E18.5, mutants display highly abnormal, reduced tracheal rings
|
hematopoietic system
|
|
• at E18.5, nine of 10 mutants exhibit display aplasia or significant hypoplasia of the thymus
|
|
|
• at E18.5, nine of 10 mutants exhibit display aplasia or significant hypoplasia of the thymus
|
cellular
|
|
• at E9.5, mutant embryos show abnormal NCC patterning caudally to the second branchial arch; instead of forming separate streams colonizing the third and fourth to sixth arches, NCCs are arranged in a single mass which is poorly connected with the hindbrain
• in contrast, the migratory pathways of more rostral NCC populations (i.e. toward branchial arches 1 and 2) appear normal
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Aldh1a2tm1Dll mutation
(0 available);
any
Aldh1a2 mutation
(36 available)
Aldh1a2tm1Ipc mutation
(0 available);
any
Aldh1a2 mutation
(36 available)
Tg(Rarb-cre)1Mrc mutation
(1 available)
|
|
|
limbs/digits/tail
|
|
• abnormal flexure of the forepaw digits, especially of second and third digits
|
|
|
• partial syndactyly of the second to forth forelimb digits
|
muscle
|
N |
• no defect in the size and topology of distal limb muscle groups and their intersections, except for a slight hypoplasia of the extensor radialis muscles
|
skeleton
|
N |
• no defect in digit skeleton
|
nervous system
|
|
• an early embryonic loss of a subset of Lim1+ brachial motoneurons, a mispositioning of Islet1+ neurons and inappropriate axonal projections of the nerves innervating extensor limb muscles
|



 Analysis Tools
Analysis Tools