Phenotypes associated with this allele
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Scn1atm1.1Aesc mutation
(0 available);
any
Scn1a mutation
(114 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• 50% mortality by P10.5 and 100% lethality by P25
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Scn1atm1.1Aesc mutation
(0 available);
any
Scn1a mutation
(114 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• average life span is 18.5 days with mice dying between P16 and P26
|
nervous system
|
N |
• mice exhibit normal neuronal cell abundance and cell viability
|
|
|
• mice exhibit visible seizures at P16 unlike wild-type mice
• seizures last 30 to 90 seconds and consist of excessive jumping, repetitive jerking of all four limbs, head nodding, and clonus of the forelimbs and tail unlike wild-type mice
|
|
|
• observed in some seizures
|
|
|
• mice exhibit decreased threshold and latency to onset of tonic febrile seizure compared with similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
• mice exhibit decreased threshold and latency to onset of tonic febrile seizure compared with similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
• Gaba-ergic interneurons exhibit decreased action potential firing compared with wild-type mice
|
|
|
• mice exhibit a trend towards increased current density in GABA-ergic pyramidal neurons and a decrease in total sodium current amplitude in bipolar neurons compared with wild-type cells
• after repeated depolarization, GABA-ergic neurons exhibit a greater decrease in current than in wild-type neurons and slower recovery from inactivation
|
growth/size/body
behavior/neurological
|
|
• mice exhibit visible seizures at P16 unlike wild-type mice
• seizures last 30 to 90 seconds and consist of excessive jumping, repetitive jerking of all four limbs, head nodding, and clonus of the forelimbs and tail unlike wild-type mice
|
|
|
• observed in some seizures
|
|
|
• mice exhibit decreased threshold and latency to onset of tonic febrile seizure compared with similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
• mice exhibit decreased threshold and latency to onset of tonic febrile seizure compared with similarly treated wild-type mice
|
Allelic
Composition |
Scn1atm1.1Aesc/Scn1a+
|
|
Genetic
Background |
involves: 129S6/SvEvTac * 129X1/SvJ * C57BL/6J |
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Scn1atm1.1Aesc mutation
(0 available);
any
Scn1a mutation
(114 available)
|
|
|
behavior/neurological
|
|
• average latency to flurothyl-induced generalized tonic-clonic seizures is 21% shorter than in wild-type mice, indicating reduced thresholds to induced seizures
|
nervous system
|
|
• average latency to flurothyl-induced generalized tonic-clonic seizures is 21% shorter than in wild-type mice, indicating reduced thresholds to induced seizures
|
Allelic
Composition |
Scn1atm1.1Aesc/Scn1a+
|
|
Genetic
Background |
involves: 129X1/SvJ * C57BL/6J * SJL |
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Scn1atm1.1Aesc mutation
(0 available);
any
Scn1a mutation
(114 available)
|
|
|
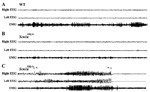
Spontaneous seizure in an Scn1atm1.1Aesc/Scn1a+ mouse
nervous system
|
|
• mice exhibit low levels of spontaneous generalized seizures characterized by stereotypic motor behaviors unlike wild-type mice
|
|
|
• latency to generalized tonic clonic seizures induced by flurothyl is reduced compared to in similarly treated wild-type mice
• however, treatment with valporic acid (VPA) restores latency to normal and susceptibility to kainic acid-induced seizures is normal
|
|
|
• mice exhibit decreased threshold and latency to onset of tonic febrile seizure compared with similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
• mice exhibit decreased threshold and latency to onset of tonic febrile seizure compared with similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
• latency to generalized tonic clonic seizures induced by flurothyl is reduced compared to in similarly treated wild-type mice
• however, treatment with valporic acid (VPA) restores latency to normal
|
|
|
• seizures are associated with spike discharges at least two times the amplitude of background unlike in wild-type mice
|
|
|
• mice exhibit a trend towards increased current density in GABA-ergic pyramidal neurons and a decrease in total sodium current amplitude in bipolar neurons compared with wild-type cells
• after repeated depolarization, GABA-ergic neurons exhibit a greater decrease in current than in wild-type neurons and slower recovery from inactivation
|
behavior/neurological
|
|
• mice exhibit low levels of spontaneous generalized seizures characterized by stereotypic motor behaviors unlike wild-type mice
|
|
|
• latency to generalized tonic clonic seizures induced by flurothyl is reduced compared to in similarly treated wild-type mice
• however, treatment with valporic acid (VPA) restores latency to normal and susceptibility to kainic acid-induced seizures is normal
|
|
|
• mice exhibit decreased threshold and latency to onset of tonic febrile seizure compared with similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
• mice exhibit decreased threshold and latency to onset of tonic febrile seizure compared with similarly treated wild-type mice
|
|
|
• latency to generalized tonic clonic seizures induced by flurothyl is reduced compared to in similarly treated wild-type mice
• however, treatment with valporic acid (VPA) restores latency to normal
|
|
|
• seizures are associated with spike discharges at least two times the amplitude of background unlike in wild-type mice
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Kcnq2Nmf134 mutation
(1 available);
any
Kcnq2 mutation
(47 available)
Scn1atm1.1Aesc mutation
(0 available);
any
Scn1a mutation
(114 available)
|
|
|
behavior/neurological
|
|
• mutants begin to display spontaneous generalized seizures starting at P16, most being myoclonic jerks, a few generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and one mouse showing partial motor seizure
• generalized seizures are periodically followed by tonic extension of the hindlimbs
|
|
|
• mutants show a few generalized tonic-clonic seizures
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• 47% of mutants survive for more than 100 days
|
|
|
• sporadic death begins to occur at P19, with 42% mortality by P25
|
nervous system
|
|
• mutants begin to display spontaneous generalized seizures starting at P16, most being myoclonic jerks, a few generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and one mouse showing partial motor seizure
• generalized seizures are periodically followed by tonic extension of the hindlimbs
|
|
|
• mutants show a few generalized tonic-clonic seizures
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Scn1atm1.1Aesc mutation
(0 available);
any
Scn1a mutation
(114 available)
Scn8amed-jo mutation
(1 available);
any
Scn8a mutation
(99 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• 47% of mutants survive for over 100 days
|
Allelic
Composition |
Scn1atm1.1Aesc/Scn1a+
Scn8amed-jo/Scn8a+
|
|
Genetic
Background |
involves: 129S6/SvEvTac * 129X1/SvJ * C57BL/6J * DBA/2WyDi |
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Scn1atm1.1Aesc mutation
(0 available);
any
Scn1a mutation
(114 available)
Scn8amed-jo mutation
(1 available);
any
Scn8a mutation
(99 available)
|
|
|
behavior/neurological
|
N |
• average latency to flurothyl-induced generalized tonic-clonic seizures is 50% longer when compared to single heterozygous Scn1a mice, but no different from wild-type indicating that seizure thresholds are restored to normal levels
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Scn1atm1.1Aesc mutation
(0 available);
any
Scn1a mutation
(114 available)
Tg(Eno2-Scn2a1*)Q54Mm mutation
(0 available)
|
|
|
behavior/neurological
|
|
• mutants begin to exhibit spontaneous partial motor seizures and generalized tonic-clonic seizures at P16
• general seizures last 45-100 seconds, during which time mice experience repetitive jerking of all four limbs and neck, running, and jumping, and tail clonus; seizures often end with tonic hindlimb extension, indicative of a severe seizure
|
|
|
• mutants begin to exhibit generalized tonic-clonic seizures at P16
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• sporadic death begins to occur at P16, with 100% mortality by P24
|
nervous system
|
|
• mutants begin to exhibit spontaneous partial motor seizures and generalized tonic-clonic seizures at P16
• general seizures last 45-100 seconds, during which time mice experience repetitive jerking of all four limbs and neck, running, and jumping, and tail clonus; seizures often end with tonic hindlimb extension, indicative of a severe seizure
|
|
|
• mutants begin to exhibit generalized tonic-clonic seizures at P16
|



