Phenotypes associated with this allele
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Rae1tm1Jvd mutation
(0 available);
any
Rae1 mutation
(23 available)
|
|
|
mortality/aging
|
|
• homozygous embryos are present at E3.5 but absent by E8.5
|
embryo
|
|
• in culture the inner cell mass fails to expand from E6.5 to E8.5 and instead degenerates
• however, the trophoblast cells develop normally
|
Allelic
Composition |
Rae1tm1Jvd/Rae1+
|
|
Genetic
Background |
Not Specified |
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Rae1tm1Jvd mutation
(0 available);
any
Rae1 mutation
(23 available)
|
|
|
cellular
|
|
• in heterozygous MEFs after 5 passages about 20% of metaphases are aneuploid compared to about 9% in wild-type cells and a wider range of nonmodal chromosome numbers is seen
(J:81546)
• at 5 months of age, 9% of splenocytes are aneuploid
(J:81546)
• the number of aneuploid splenocytes increases from 9% at 5 months to 33% at 24 months compared to only 3% in wild-type mice at 35 months
(J:105717)
|
|
|
• after 12 hours of treatment with 200 ng/ml nocodazole (induces spindle damage) only 2.5% of heterozygous MEFs are arrested compared to 15% of wild-type cells and after 4 hours in serum without nocodazole (recovery phase) more cells are present with 4N DNA content suggesting progression to G1 without cell division
(J:81546)
• overexpression of Rae1 can rescue the mitotic checkpoint defect
(J:81546)
• after nocodazole treatment the time for 50% of cells to exit prometaphase arrest is reduced to 3 hours compared to 7.2 hours for wild-type MEFs
(J:105717)
|
|
|
• lagging chromosomes are seen in 5% of anaphase figures compared to 2% of wild-type figures
(J:81546)
• in splenocytes prematurely separated sister chromatids increase from 0 at 5 months to being present in 10-11% of metaphases at 24-27 months compared to 0 at 27 months and only 4% at 35 months in wild-type
(J:105717)
• however, no chromosome breaks or fusions are seen at 24 months of age
(J:105717)
|
neoplasm
|
|
• a single application of 50 ul of 0.5% DMBA at P5 results in an increased incidence of lung tumors and more tumors per animal in heterozygotes compared to wild-type mice
• however, no difference in spontaneous tumor incidence is seen compared to wild-type mice
|
homeostasis/metabolism
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Nup88em1Jvd mutation
(0 available);
any
Nup88 mutation
(44 available)
Nup98tm1Jvd mutation
(0 available);
any
Nup98 mutation
(146 available)
Rae1tm1Jvd mutation
(0 available);
any
Rae1 mutation
(23 available)
|
|
|
cellular
|
|
• chromosome segregation errors are reduced to 18% from 37% in double Rae1tm1Jvd Nup98tm1Jvd heterozygotes and the mitotic checkpoint is fully restored
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Bub3tm1Jvd mutation
(0 available);
any
Bub3 mutation
(23 available)
Rae1tm1Jvd mutation
(0 available);
any
Rae1 mutation
(23 available)
|
|
|
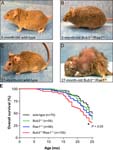
Reduced lifespan, cataract, lordokyphosis and cachexia in Bub3tm1Jvd/Bub3+ Rae1tm1Jvd/Rae1+ mice
mortality/aging
|
|
• seen in the second year of life
|
cellular
|
|
• in double heterozygous MEFs after 5 passages aneuploid cells are increased by 32% compared to wild-type cells and a wider range of nonmodal chromosome numbers is seen compared to single heterozygous or wild-type MEFs
(J:81546)
• at 5 months of age, 37% of splenocytes are aneuploid compared to 9% in single heterozygotes
(J:81546)
• the number of aneuploid splenocytes increases from 37% at 5 months to 47% at 24 months compared to only 3% in wild-type mice at 35 months
(J:105717)
|
|
|
• after nocodazole treatment the time for 50% of cells to exit prometaphase arrest is reduced to 2.2 hours compared to 7.2 hours for wild-type MEFs
|
|
|
• prematurely separated sister chromatids are seen in 19% and 13% of mitotic figures from MEFs and splenocytes (at 5 months of age), respectively
(J:81546)
• lagging chromosomes are seen in 15% of anaphase figures compared to 5% of single heterozygous and 2% of wild-type figures
(J:81546)
• in splenocytes prematurely separated sister chromatids increase from 14% at 5 months to being present in 24% of metaphases at 24 months compared to 0 at 27 months and only 4% at 35 months in wild-type
(J:105717)
• however, no chromosome breaks or fusions are seen at 24 months of age
(J:105717)
• 47% of anaphases have multiple lagging chromosomes compared to 0% in wild-type MEFs
(J:105717)
|
|
|
• double heterozygous MEFs grow slower than single heterozygous or wild-type MEFs
|
|
|
• at passage 5 and 7 increased expression of senescence related genes in MEFs is seen
• at passage 7 but not passage 3, double heterozygous MEFs grow slower than single heterozygous or wild-type MEFs
|
adipose tissue
|
|
• decreased thickness of the subcutaneous adipose tissue
|
|
|
• at 27 months of age a dramatic decrease in body fat is seen
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• body weight is similar to wild-type at 5 months of age but significantly lower by 24 months of age
|
muscle
|
|
• clear signs of skeletal muscle degeneration and atrophy are seen in mice with lordokyphosis
|
|
|
• clear signs of skeletal muscle degeneration and atrophy are seen in mice with lordokyphosis
|
skeleton
|
|
• lordokyphosis is seen at an earlier age and with increased severity compared to single heterozygous or wild-type mice
|
vision/eye
|
|
• incidence of cataract formation is increased and the latency is decreased compared to single heterozygotes
|
neoplasm
|
|
• a single application of 50 ul of 0.5% DMBA at P5 results in an increased incidence of lung tumors and more tumors per animal in double heterozygotes compared to wild-type mice
• however, no difference in spontaneous tumor incidence is seen compared to wild-type mice
|
homeostasis/metabolism
integument
|
|
• decreased thickness of the subcutaneous adipose tissue
|
|
|
• from 5 to 27 months of age dermal thickness decreases by 21% lower compared a decrease of 9% in wild-type mice
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Nup98tm1Jvd mutation
(0 available);
any
Nup98 mutation
(146 available)
Rae1tm1Jvd mutation
(0 available);
any
Rae1 mutation
(23 available)
|
|
|
cellular
|
|
• MEFs exhibit mitotic checkpoint defects
|
|
|
• MEFs have increased rates of chromatin bridges and lagging chromosomes indicating chromosome segregation errors
• incomplete centrosome separation is increased in MEFs
• MEFs treated with the PLK1 inhibitor BI2536 show restoration of normal centrosome separation
|
|
|
• MEFs exhibit more frequent spindle geometry defects showing mitotic spindle asymmetry
|



 Analysis Tools
Analysis Tools