|
|
|
|
|
|
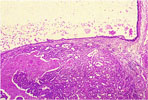
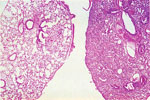
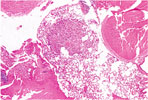
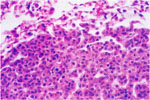
| 97. Gall Bladder Carcinoma |
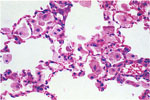
98.
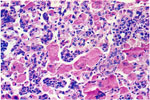
Eosinophilic Crystals -Pulmonary Alveolar Macrophages |
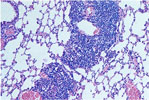
99.
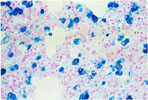
Chronic Passive Congestion (Prussian Blue Stain) -Lung |
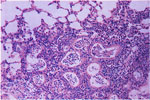
100.
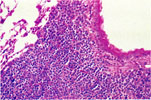
Perivascular and Peribronchial Lymphoid Aggregates -Lung |
101. Pulmonary Atelectasis Adjacent to Normal Lung | 102. Pulmonary Alveolar Macrophage Accumulations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
103.
Mycoplasma pulmonis Infection -Lungs |
104.
Chronic Sendai Virus Infection -Lungs |
105. Pulmonary Alveolar Cell Adenoma | 106. Pulmonary Alveolar Cell Adenoma |
107.
Adenoma -Pulmonary Surfactant Apoprotein -Lung |
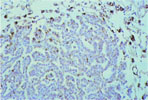
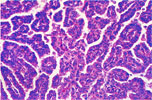
108.
Papillary Adenocarcinoma -Lung |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
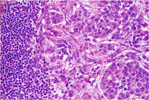
109.
Lymph Node Metastasis of Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma -Lung |
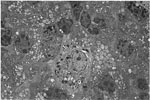
110.
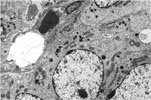
Electron Micrograph -Pulmonary Alveolar Type II Adenoma |
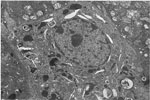
111.
Electron Micrograph -Pulmonary Alveolar Type II Adenoma |
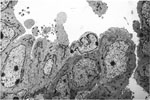
112.
Electron Micrograph -Papillary Adenocarcinoma -Lung |
113.
Electron Micrograph -Papillary Adenocarcinoma -Lung |
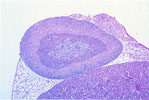
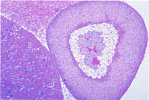
114.
X-Zone -Adrenal Cortex |
|
|
|
|
|
|
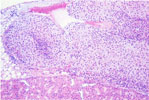
| 115. Adrenocortical Vacuolization (X-Zone) | 116. Accessory Adrenocortical Nodule | 117. Subcapsular Adrenocortical Spindle Cell Hyperplasia |
118.
Ceroid Pigment -Macrophages -Zona reticularis -Adrenal (H & E) |
119.
Ceroid Pigment -Adrenal (PAS) |
120. Adrenocortical Adenoma (Type A Spindle Cell) |
| Back |